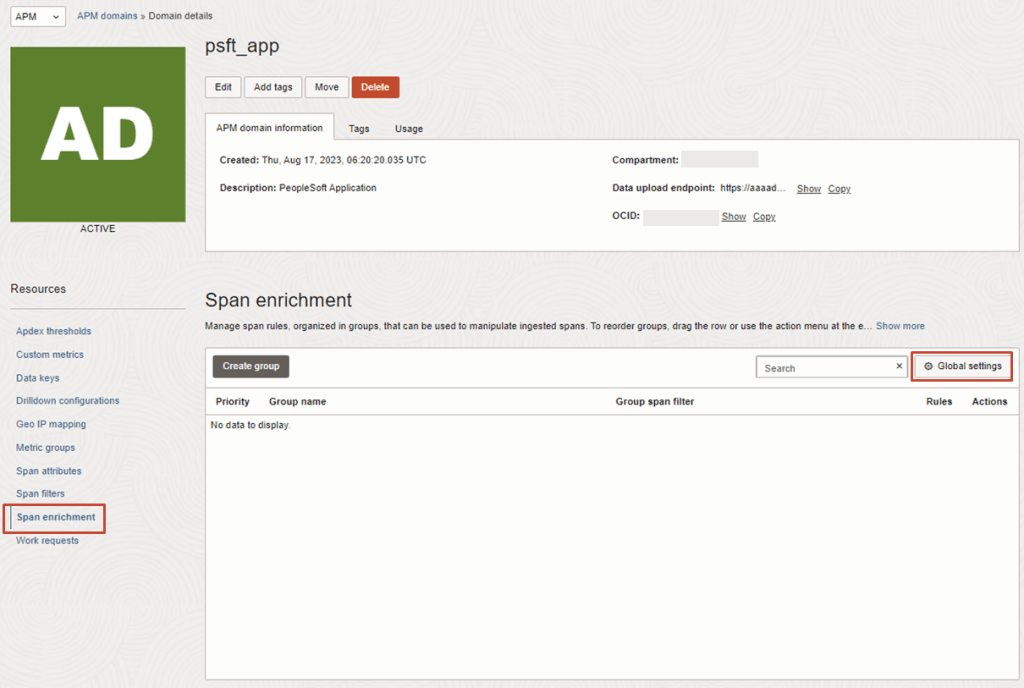
The OCI Application Performance Monitoring (APM) service enables administrators to monitor and observe the PeopleSoft web applications.
It provides deep visibility into the application performance from end-user experience down through to the application server requests.
For many customers, the PeopleSoft (PSFT) Application is critical to business operations. With OCI Application Performance Monitoring (APM) service, administrators can:
- Analyze all end user experience with accessing PeopleSoft web pages.
- Trace transactions across various components and isolate problems to the impacting application or infrastructure tier.
- Has ability to drill into application code.
- Generally, APM tools cannot drill into the SQL code for the PeopleSoft application. This inability occurs is because, the SQL call is performed in the Tuxedo layer. However, OCI APM service offers a unique feature to overcome this limitation. It can perform instrumentation of outbound JOLT calls from WebLogic to Tuxedo. This helps at least understand how much time is spent in this layer.
- Easily Capture End Username for user sessions without modifying application code
- Search in context based on PeopleSoft attributes including:
– Portal Name
– Portal Object Name
– and more